TreeSet 是一种可有序存放元素的集合,HashSet 是 value 为固定值的 HashMap,TreeSet 是 value 为固定值得 TreeMap。
TreeMap
┌───┐ |
HashMap 利用了 hashCode,TreeMap 则利用了树,一个二叉树。
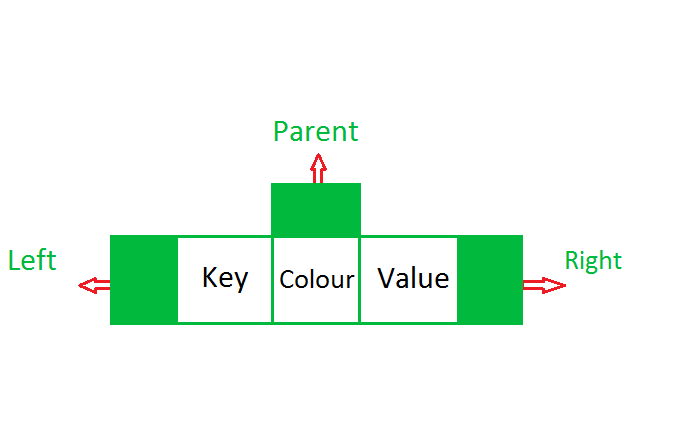
比较 Key
TreeMap 的有序通过比较 key 来实现,无法利用 hashCode 来比较,它需要有一个比较 key 的规则。可通过 Key 继承 Comparable 接口或设置 Comparator 来提供。
Integer
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> { |
String
public final class String |
自定义类
使用 Comparator
// A class to represent a student. |
输出
TreeMap using TreeMap(Comparator) constructor: |
使用 Comparable
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ |
如何排序
添加时,跟 root 节点比较,小于放到左边,大于放到右边。
public V put(K key, V value) { |
时间复杂度
针对二叉树,4 层的总节点:2^0^ + 2^1^ + 2^2^ + 2^3^ -> 2^4^,如果树节点数为 n,树的高度为 log(n)。
所以 TreeMap 的查找和新增时间复杂度为 O(log(n))。
vs LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 使用一个额外双向链表,记录插入顺序,所以它是根据插入顺序排序。